Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, autoimmune disease that affects your joints and causes pain, swelling, stiffness, and loss of mobility. It can also cause inflammation throughout the body, leading to other medical problems. It’s estimated that about a million Americans have it. Here’s what you need to know about it.
How Does RA Develop?
Rheumatoid arthritis begins with an abnormal response from your immune system. Usually, your immune system helps protect you from infection or illness by attacking foreign substances in your body. But with RA, your immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues in the joints and surrounding areas. This process causes inflammation that can damage the cartilage and bone in the joints over time.
RA develops over time, so that means that it has its own set of risk factors. Here are some of them:
Gender
Women are more likely to develop rheumatoid arthritis than men; women are three times as likely to be affected by the condition. This could be due to hormonal factors or lifestyle choices such as smoking or drinking alcohol, which increase your risk for RA.
Age
Rheumatoid arthritis tends to affect people between 40 and 60 years old, although it can affect people of any age. As you get older, your risk of developing RA increases. It is also worth noting that RA can develop more quickly in people over 65.
Family History
If someone in your family has been diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, you may have a higher chance of developing the condition yourself. This could be because specific genes appear to make some people susceptible to the disease, though further research is still needed.
Environmental Factors
Prolonged exposure to certain environmental toxins, such as asbestos or silica, may also increase your risk for RA. However, it is unclear how much these substances contribute to the development of the disease. Additionally, smoking cigarettes has been linked with an increased risk for RA, so if you smoke, you must quit as soon as possible to reduce your chances of developing this condition.
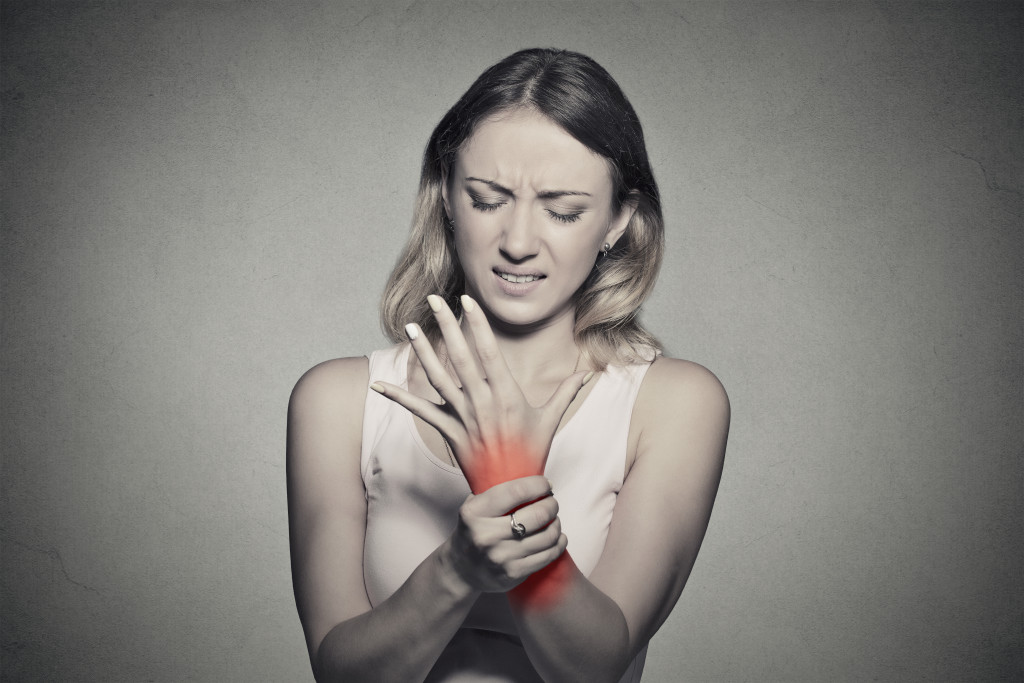

What Are The Symptoms Of RA?
The most common symptom of RA is joint pain and swelling. You may also experience loss of motion in the affected joints, fatigue, fever, and weight loss. In some cases, people with RA can also develop nodules under their skin near their elbows or knuckles. These are called rheumatoid nodules, usually painless, but they can be tender if inflamed or infected.
Moreover, studies have found a link between RA and oral health. Those with RA can experience mouth sores, difficulty opening or closing the mouth, a change in how their teeth fit together, and tooth loss. Therefore, people with RA must get a robust replacement tooth. This will ensure that they experience less oral pain and problems because the tooth can protect the mouth’s gums and other soft tissues.
How Is RA Treated?
There is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, but treatments are available to help reduce symptoms and slow disease progression. These treatments include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). These medications can help reduce inflammation and pain and slow down joint damage caused by the disease. Other treatments may include physical therapy, lifestyle changes such as exercise or rest, heat/cold therapy, or assistive devices such as splints or braces to support weak joints.
Prevention
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are ways you can prevent RA:
Exercise Regularly
Regular exercise is one of the best ways to prevent rheumatoid arthritis, as it strengthens muscles and joints and helps maintain a healthy weight. Exercise also improves circulation throughout the body, which helps ensure that all joints receive adequate nutrition and oxygen. The American College of Rheumatology recommends at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity five days per week for adults who want to prevent rheumatoid arthritis.
Eat a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet full of vitamins and minerals can help reduce inflammation, protect joint health, and reduce the risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats like avocado oil can provide your body with all the nutrients it needs to stay healthy and strong. Additionally, limit your intake of processed foods high in sugar and unhealthy fats, as these have been linked to an increased risk for autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects many people worldwide. While there is no cure for this condition, treatments are available to help manage its symptoms and slow down its progression. If you think you may have RA, it’s essential to talk to a doctor so they can evaluate your symptoms and determine what treatment options will be best for you. With proper treatment, individuals with RA can still lead an active life despite having this condition.